(!)Due to Microsoft's end of support for Internet Explorer 11 on 15/06/2022, this site does not support the recommended environment.
Instead, please kindly use other browsers like Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge or Mozilla Firefox.
50,000 Stock items for Same Day Ship Out.
All Categories
Categories
- Automation Components
A wide variety of standard and configurable components for factory automation engineers in industries such as automotive, semiconductor, packaging, medical and many more.
- Linear Motion
- Rotary Motion
- Connecting Parts
- Rotary Power Transmission
- Motors
- Conveyors & Material Handling
- Locating, Positioning, Jigs & Fixtures
- Inspection
- Sensors, Switches
- Pneumatics, Hydraulics
- Vacuum Components
- Hydraulic Equipment
- Discharging / Painting Devices
- Pipe, Tubes, Hoses & Fittings
- Modules, Units
- Heaters, Temperature Control
- Framing & Support
- Casters, Leveling Mounts, Posts
- Doors, Cabinet Hardware
- Springs, Shock Absorbers
- Adjusting, Fastening, Magnets
- Antivibration, Soundproofing Materials, Safety Products
- Fasteners
A good selection of accessories such as screws, bolts, washers and nuts that you may need for your daily engineering usage.
- Materials
Browse industrial materials ranging from heat insulating plates, sponges, to metal and plastic materials in different sizes to meet your various applications.
- Wiring Components
A wide variety of wiring parts for connecting and protecting control and PC parts including Connectors, Cables, Electric Wires, Crimping Terminals and more.
- LAN Cables / Industrial Network Cables
- Cables by Application
- Cables with Connectors
- RS232 / Personal Computers / AV Cables
- Wires/Cables
- Connectors (General Purpose)
- Crimp Terminals
- Zip Ties
- Cable Glands
- Cable Bushings/Clips/Stickers
- Screws/Spacers
- Cable Accessories
- Tubes
- Protection Tubes
- Ducts/Wiremolds
- General Purpose Tools
- Dedicated Tools
- Soldering Supplies
- Electrical & Controls
A wide variety of controls and PC parts for electrical engineers including Controls, Powers, PC parts and more.
- Cutting Tools
A wide variety of cutting tools for many uses and work materials including End Mills, Drills, Cutters, Reamers, Turning Tools and more.
- Carbide End Mills
- HSS End Mills
- Milling Cutter Inserts/Holders
- Customized Straight Blade End Mills
- Dedicated Cutters
- Turning Tools
- Drill Bits
- Screw-Hole-Related Tools
- Reamers
- Chamfering / Centering Tools
- Fixtures Related to Cutting Tools
- Step Drills
- Hole Saws
- Clean Key Cutters
- Core Drills (Tip Tools)
- Magnetic Drilling Machine Cutters
- Drill Bits for Electric Drilling Machines
- Woodworking Drill Cutters
- Drills for Concrete
- Processing Tools
A wide variety of tools and supplies used in processing including Machine Tools, Measurement Tools, Grinding and Polishing Supplies and more.
- Material Handling & Storage
A wide variety of goods used in shipment, material handling and warehouse including Tape supplies, Stretch film, Truck, Shelf, Crane and more.
- Tape Supplies
- Cushioning Materials
- Stretch Films
- Cardboard
- Plastic Bags
- PP Bands
- Magic Tapes / Tying Belts
- Rubber Bands
- Strings/Ropes
- Cable Ties
- Tags
- Labelers
- Unpacking Cutters
- Packing Support Equipment
- Cloth Sheets for Packing
- Conveyance/Dolly Carts
- Tool Wagons
- Tool Cabinets / Container Racks
- Lifters / Hand Pallets
- Container Pallets
- Storage Supplies
- Shelves/Racks
- Work Benches
- Suspended Clamps/Suspended Belts
- Jack Winches
- Chain Block Cranes
- Bottles/Containers
- Bicycle Storage Area
- Safety & General Supplies
A large variety of goods for every kind of factories and offices including Protection items, Cleaning supplies, sanitations, office supplies and more.
- Lab & Clean Room Supplies
A large variety of items used in R&D and Clean Room including research Equipment, Laboratory Essentials, Analysis Supplies, Clean Environment-Related Equipment and more.
- Press Die Components
Choose from thousands of standard stamping die components including Punch & Die, Gas Springs, Guide Components, Coil Springs and many more.
- Plastic Mold Components
Browse our wide variety of mold components including Ejector Pins, Sleeves, Leader Components, Sprue Bushings and many more.
- Ejector Pins
- Sleeves, Center Pins
- Core Pins
- Sprue bushings, Gates, and other components
- Date Mark Inserts, Recycle Mark Inserts, Pins with Gas Vent
- Undercut, Plates
- Leader Components, Components for Ejector Space
- Mold Opening Controllers
- Cooling or Heating Components
- Accessories, Others
- Components of Large Mold, Die Casting
- Injection Molding Components
Browse our injection molding components including Heating Items, Couplers, Hoses and more.
- Injection Molding Machine Products
- Accessories of Equipment
- Auxiliary Equipment
- Air Nippers
- Air Cylinders
- Air Chuck for Runner
- Chuck Board Components
- Frames
- Suction Components
- Parallel Air Chuck
- Special Air Chuck
- Chemical for Injection Molding
- Mold Maintenance
- Heating Items
- Heat Insulation Sheets
- Couplers, Plugs, One-touch Joints
- Tubes, Hoses, Peripheral Components
Search by Application
Brands
- Scheduled Maintenance Notice: This site will be unavailable due to scheduled maintenance from 9:00 24/11/2024 to 7:00 (SGT) 25/11/2024. We apologize for the inconvenience.
- Notice of End of Sales for Economy Series Pneumatic Equipment Category. More information.
In-Line Type Vacuum Ejector ZU□A Series

- Volume Discount
An ejector manufactured by SMC.
[Features]
• Vacuum port and supply port are located collinear to each other to facilitate easy piping.
· Lightweight, as the body is made of resin.
(i)Caution
- Please refer to the catalog for specification details.
- The product images may be representative images only. Please refer to the manufacturer's catalog for shape details.
Japanese Only
Part Number
Configured Part Number is shown.
Vacuum Ejector In-Line Type ZU Series Specifications

ZU05□/ZU07□ external appearance
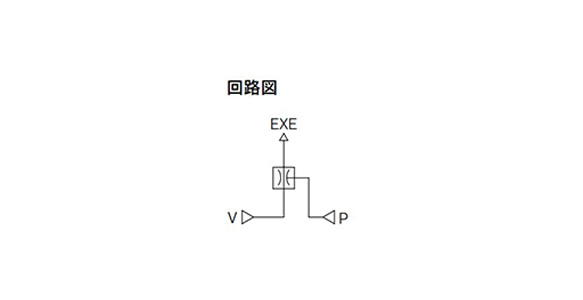
ZU Series circuit drawing
Ejector Specifications *1
| Type | Model | Nozzle Diameter mm | Maximum Vacuum Pressure kPa *2 | Maximum Suction Flow Rate L/min (ANR) *2 | Air Consumption L/min (ANR) *2 | Weight g |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| High Vacuum Type | ZU05S | 0.5 | -84 | 7 | 14 | 6.5 |
| ZU07S | 0.7 | -84 | 10 | 29 | 7.0 | |
| High Flow Rate Type | ZU05L | 0.5 | -48 | 12 | 14 | 6.5 |
| ZU07L | 0.7 | -48 | 16 | 29 | 7.0 |
- *1 The values indicating characteristics are representative values and may vary depending on the atmospheric pressure (weather, altitude, etc.)
- *2 Value at a supply pressure of 0.45 MPa
Structural Drawing
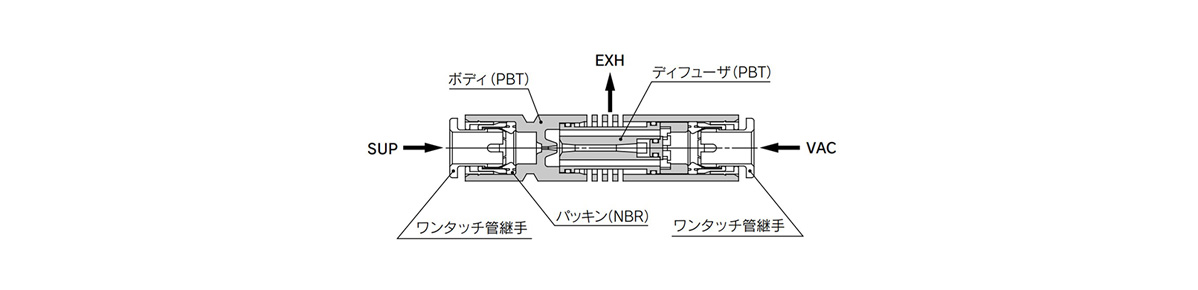
ZU Series structural drawing
Drawing
(Unit: mm)
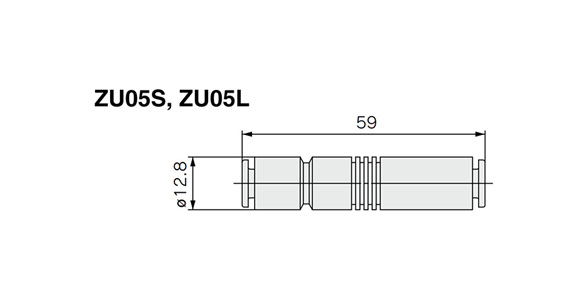
ZU05S, ZU05L dimensional drawing
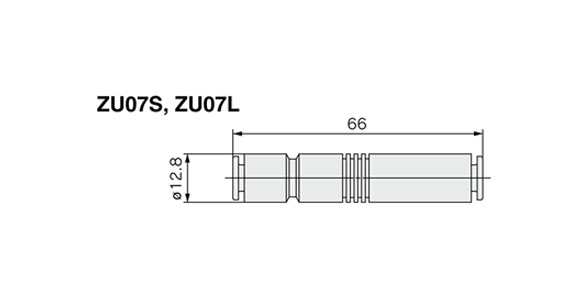
ZU07S, ZU07L dimensional drawing
Exhaust Characteristics / Flow Rate Characteristics (Representative Values)*
ZU05S
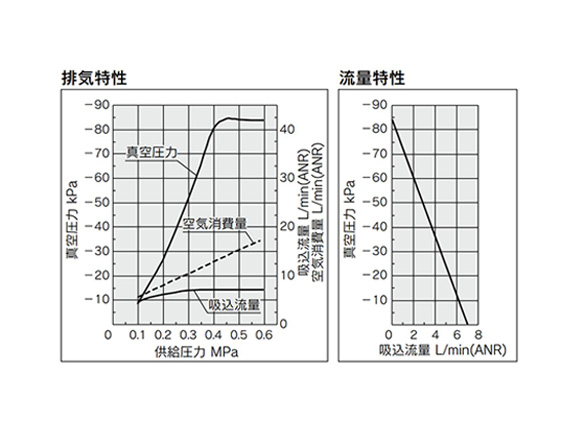
ZU05S exhaust characteristics (left) / flow rate characteristics (right) graph
ZU05L
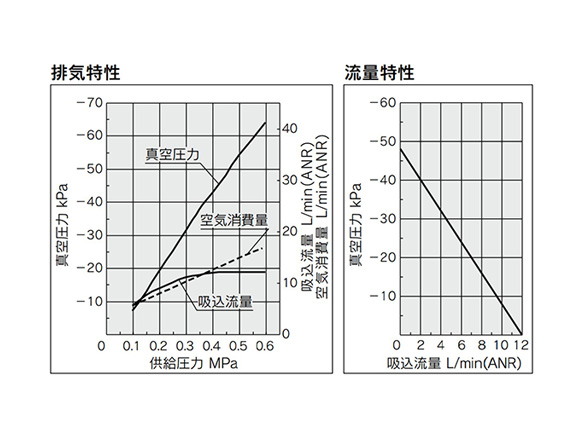
ZU05L exhaust characteristics (left) / flow rate characteristics (right) graph
ZU07S
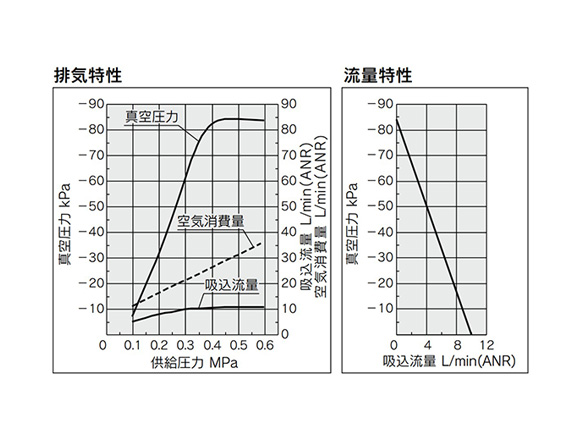
ZU07S exhaust characteristics (left) / flow rate characteristics (right) graph
ZU07L
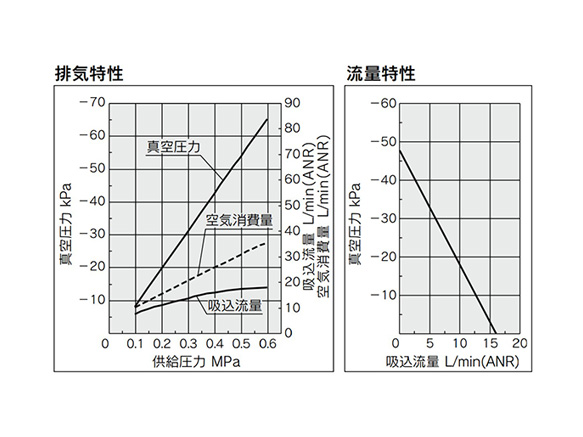
ZU07L exhaust characteristics (left) / flow rate characteristics (right) graph
*Flow rate characteristics are with a supply pressure of 0.45 MPa.
How to Read Flow Rate Characteristics Graphs
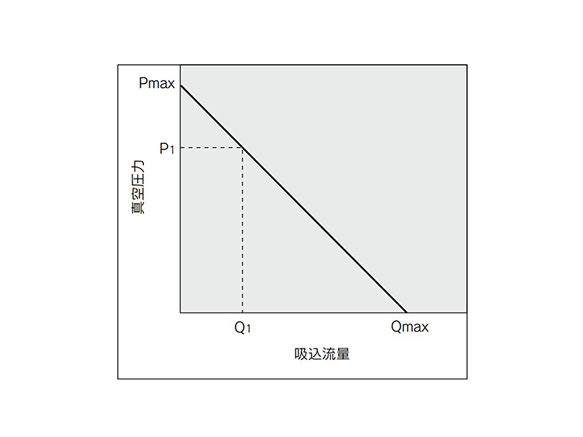
The flow rate characteristics show the relationship between the vacuum pressure and the suction flow rate of the ejector. It also shows that as the suction flow rate changes, so too does the vacuum pressure.
Generally, the relationship shown is at the standard working pressure for the ejector.
In the diagram, Pmax denotes the maximum vacuum pressure, and Qmax denotes the maximum suction flow rate. These values are the values listed as the specifications in the manufacturer's catalog and elsewhere.
See below for information on how to change the vacuum pressure.
- 1. When the ejector suction port is closed and sealed, the suction flow rate is 0 and the vacuum pressure is at its maximum (Pmax).
- 2. As the suction port is gradually opened and air begins to flow (leak), the suction flow rate increases and the vacuum pressure decreases. (State of P1 and Q1)
- 3. As the suction port opens further and on to the fully opened state, the suction flow rate reaches its maximum value (Qmax), and the vacuum pressure becomes close to 0 (atmospheric pressure). Thus, as the suction flow rate changes, so too does the vacuum pressure. In other words, if there is no leak in the vacuum port, the vacuum pressure will be at its highest level. As the leakage amount increases, the vacuum pressure decreases and becomes close to 0 when the leakage amount and the maximum suction flow rate become equal. Be aware that when suctioning a workpiece that is breathable or has a leak, the vacuum pressure will not be very high.
Notes
Mounting
- Be careful not to apply an excessive load or generate moments to the ejector body via the connection port or by mounting.
- Refer to the manufacturer's catalog for selection and sizing.
Cautions for Handling One-Touch Fittings
One-Touch Fitting Tube Connection and Disconnection
- Tube attachment
- 1. Cut the tube at a right-angle. The tube must not have any cuts on its periphery. Use tube cutters TK-1, 2 and 3 when cutting tubes. Do not use pliers, wire cutters, scissors, etc. This could result in an uneven cut or cause the tube to become flattened. This in turn might make connecting the tube difficult or result in air leakage or the tube coming out after being connected. Be sure to leave a little extra length when cutting the tube.
- 2. Hold the tube and push it in slowly until completely inserted.
- 3. After inserting the tube, pull it lightly to make sure it does not become detached. Failure to make sure the tube is fully inserted may cause air to leak or the tube to come out.
- Tube removal
- 1. Push-in the release bushing with sufficient force. At the same time, evenly press in the collar.
- 2. Keep the release bushing held in so that it does not retract and then pull out the tube. If the release bushing is not being pushed in sufficiently, the tube may become too tightly gripped and make it difficult to pull out.
- 3. Detached tubes can be reused by cutting off the section that was previously gripped. Reusing the tube without cutting off the gripped section may lead to air leakage and make it difficult to remove the tube.
Other notes
- *See the manufacturer's catalog for information not detailed above.
- *The images are for representative model numbers only.
| Part Number |
|---|
| ZU05LA01 |
| ZU05SA01 |
| ZU07LA01 |
| ZU07SA01 |
| Part Number | Standard Unit Price | Minimum order quantity | Volume Discount | Days to Ship | Ultimate Vacuum (kPa) | Air Consumption Flow Rate (l/min) | Vacuum Port Connecting Port Shape | Vacuum Port One-Touch Fitting Size | Air Supply Port Connecting Port Shape | Air Supply Port One-Touch Fitting Size | Suction Flow (l/min) | Nozzle Dia. | Overall Length B (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
- | 1 Piece(s) | Quote | -48 | 14 | Rc1/8 | - | Rc1/8 | - | 13 | 0.5mm | 67.2 | ||
SGD 30.92 | 1 Piece(s) | Available | 32 Day(s) | -90 | 14 | Rc1/8 | - | Rc1/8 | - | 7 | 0.5mm | 67.2 | |
- | 1 Piece(s) | Quote | -48 | 28 | Rc1/8 | - | Rc1/8 | - | 16 | 0.7mm | 74.2 | ||
SGD 34.07 | 1 Piece(s) | Available | 32 Day(s) | -90 | 28 | Rc1/8 | - | Rc1/8 | - | 11 | 0.7mm | 74.2 |
Loading...
Basic Information
| Type | Pipe Type | Additional Function | Not Provided | Application | Manifolds |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Operating Pressure Range(MPa) | 0.1::0.6 | Operating Temp. Range(°C) | -5::50 |
Specification/Dimensions
-
Ultimate Vacuum(kPa)
-
Air Consumption Flow Rate(l/min)
-
Vacuum Port Connecting Port Shape
- Rc1/8
- One-Touch Coupling
-
Vacuum Port One-Touch Fitting Size
-
Air Supply Port One-Touch Fitting Size
- Ø4
- Ø6
- 5/32 (Ø3.97)
-
Suction Flow(l/min)
-
Nozzle Dia.
-
Overall Length B(mm)
-
type
- ZU03
- ZU04
- ZU05
- ZU07
-
Air Supply Port Connecting Port Shape
- Rc1/8
- One-Touch Coupling
-
CAD
- 2D
- 3D
Days to Ship
-
- All
- 23 Day(s) or Less
- 31 Day(s) or Less
- 32 Day(s) or Less
Specify Alterations
- The specifications and dimensions of some parts may not be fully covered. For exact details, refer to manufacturer catalogs .



How can we improve?
How can we improve?